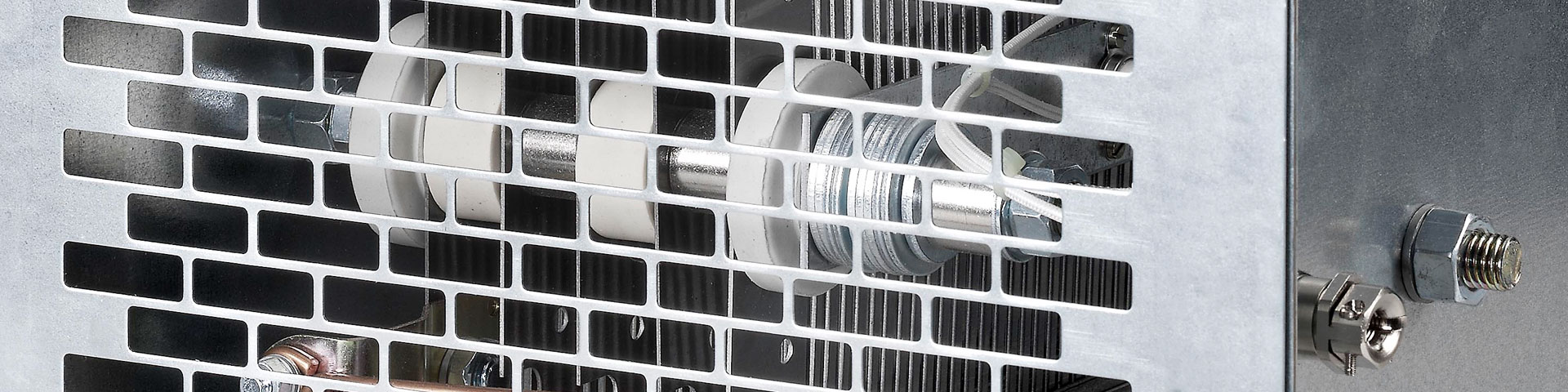
GINO excitation resistors are starting resistors for magnet coils. Magnet coils are usually wound with copper conductors. Copper has a relatively large temperature coefficient of the resistance value so that a coil at operating temperature has a resistance value that is up to 20% higher than that of a cold coil. Consequently, a magnet coil usually has a lower intrinsic resistance as compared to its nominal voltage. A starting resistor, the so-called excitation resistor, adjusts the desired operating current to be achieved at operating temperature. Moreover, excitation resistors made from a suitable resistor alloy also compensate the temperature coefficient of the total resistance in a circuit. A typical example for an excitation resistor is the field resistor of d.c. machines which adjusts the excitation current and thus the speed of a motor or the voltage of a generator. Fast response resistors are starting resistors for magnet coils that alter the pickup properties of the coils. The coil is operated with a starting resistor at a higher, mostly double, nominal voltage. The starting resistor reduces the time constant of the total circuit T = L/(Rv+Ri), results in a faster current rise and thus in a faster build-up of the magnetic field. Another way to reach this objective is to excite the coil with a high current and then insert an upstream economy resistor. However, this solution is only feasible when a change of the excited magnetic circuit results in the same magnetic induction as during the starting phase. A typical example would be the power contactor with d.c. excitation.
go back
You need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Turnstile. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Facebook. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Instagram. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Google Maps. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Google Maps. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information